Multi-Suitability Comprehensive Evaluation of Crop Straw Resource Utilization in China
-
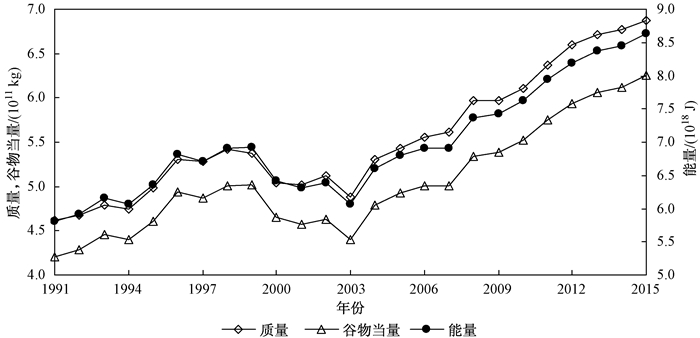
摘要: 由于作物秸秆类型不同,其营养成分和利用价值也不同,因此仅根据草谷比系数法以质量形态衡量其利用价值,难以全面直接地反映秸秆资源的多种利用价值.为综合定量评价不同利用方式下我国作物秸秆资源的各种利用价值,依据能量流动定律,构建作物秸秆多适宜性综合统一评价体系.结果表明:①以质量、能量和谷物当量3种形态综合核算我国秸秆资源量,其计量结果年际变化趋势较为一致,并且能量和谷物当量形态更能直接体现秸秆资源能源化和饲料化的实际利用价值;②1991-2015年我国作物秸秆资源利用价值总量整体上升,至2015年我国作物秸秆肥料化、基料化和原料化形态质量为6.88×1011 kg,能源化利用价值为8.89×1018 J,适宜饲料化的作物秸秆资源利用量为6.26×1011 kg谷物当量,折合当年全国粮食总产量的100.66%,因此秸秆饲料化具有较高的利用价值,并且符合当前我国"粮改饲"农业改革发展方向;③我国各地秸秆资源量在空间上呈现出显著的地域边缘属性,秸秆资源丰富地区主要集聚在华北、东北和长江中下游地区.研究显示,就作物秸秆主要利用方式而言,饲料化具有相对较高的适宜性和利用价值,但是由于经济收益、经营规模和市场供需不对称等原因,当前农户秸秆饲料化的意愿不高,可利用经济和政策等措施引导该产业有序开展.Abstract: Crop straw has different nutritional components and utilization value due to its different types. The current researches only evaluate crop straw resource comprehensive utilization in weight by the method of straw to gain ratio, however, this method is difficult to directly reflect the multiple utilization values of straw resource. Thus we built a unified quantitative estimation system based on weight, energy and cereal equivalent three forms cereal equivalent to estimate the multi-suitability utilization values of crop straw resource in China, and the main results were as follows. The inter-annual variation trend of crop straw resource accounting results in weight, energy and cereal equivalent forms were consistent, and its energy and cereal equivalent forms could directly reflect the straw actual utilization values as energy and feed, which stated that its calculation process and calculation results were scientific and effective. The total amounts of crop straw resource multiple utilization values generally increased from 1991 to 2015, the total amount of crop straw resource were 6.88×1011 kg and 8.89×1018 J in weight and energy forms, and suitable feeding crop straw resource was equal to 6.26×1011 kg in cereal equivalent form in 2015, which was 100.66% of the total grain production. Comparatively speaking, straw feed had more high utilization value, which was in keeping with the current 'grain to feed' agricultural reform and development direction in China. At the same time, the energy potentiality values of crop straw in provinces and cities in China had the distinct characteristics of marginal attribute in spatial distribution by quantitative analysis with the method of spatial auto-correlation analysis, and its straw resource-rich areas were mainly concentrated in China north, northeast, middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River region. As a whole, the potential utilization of straw resources in eastern and northern regions is higher than the western and southern regions. The study shows that the feed use has a relatively high suitability and utilization value for the main use of crop straw. However, due to its economic benefit, operation scale and market supply and demand asymmetry et al, the willingness of farmers' straw feed is not high at present, the economic and policy measures could be used to guide its industry orderly development.
-
表 1 作物秸秆资源价值估算的重要参数取值
Table 1. values of important parameter in energy accounting of crop straw resource
作物名称 可收集系数[12] 草谷比[12] 能量转换率[29]/ (106 J/kg) 稻谷秸 0.83 0.90 14.06 小麦秸 0.83 1.17 14.78 玉米秸 0.83 1.04 14.37 豆类秸 0.88 1.60 15.10 薯类秸 0.80 0.57 14.10 其他粮食秸 0.80 1.50 14.53 棉花秸* 0.90 3.00 15.09 花生秸 0.85 1.14 15.05 薯类秸 0.80 0.57 14.10 其他粮食秸 0.80 1.50 14.53 棉花秸* 0.90 3.00 15.09 花生秸 0.85 1.14 15.05 烟草秸* 0.90 0.71 15.09 甘蔗秸 0.88 0.30 2.80 甜菜秸 0.88 0.43 2.60 果蔬秸 0.60 0.10 2.40 注:*表示不适宜饲料加工的作物. 表 2 1991—2015奇数年我国作物秸秆能量的估算
Table 2. Evacuating energy potentiality of crop straw in China from 1991 to 2015 odd years
1016 J 作物名称 年份 1991 1993 1995 1997 1999 2001 2003 2005 2007 2009 2011 2013 2015 稻谷秸 193.16 186.54 194.65 210.94 208.58 186.61 168.83 189.77 195.49 205.02 211.22 213.97 218.81 小麦秸 137.79 152.78 146.77 177.05 163.54 134.81 124.2 139.94 156.96 165.31 168.59 175.09 186.95 玉米秸 122.58 127.46 138.98 129.45 158.96 141.59 143.75 172.96 189.01 203.50 239.25 271.16 278.78 豆类秸 26.52 41.47 38.01 39.88 40.27 43.65 45.24 45.88 36.58 41.04 40.58 33.92 33.80 薯类秸 17.46 20.45 20.98 20.53 23.41 22.91 22.59 22.30 18.05 19.26 21.05 21.41 21.39 其他粮食秸 29.85 32.37 29.11 26.43 21.94 19.07 19.72 18.06 15.15 12.85 14.32 15.11 16.11 棉花秸* 23.13 15.24 19.43 18.76 15.60 21.69 19.80 23.29 31.07 25.99 26.85 25.67 22.84 花生秸 9.20 12.29 14.93 14.08 18.44 21.03 19.58 20.92 19.01 21.46 23.41 24.76 23.98 油菜秸 25.67 23.96 33.75 33.06 34.98 39.12 39.42 45.06 36.50 47.15 46.35 49.91 51.54 芝麻秸 1.12 1.45 1.50 1.46 1.92 2.07 1.53 1.61 1.44 1.60 1.56 1.61 1.65 其他油料秸 5.31 5.09 4.59 4.29 6.01 5.05 6.44 6.62 3.68 6.15 7.19 7.50 8.08 麻类秸* 2.21 2.40 2.24 1.87 1.18 1.70 2.13 2.76 1.82 0.97 0.74 0.57 0.53 烟叶秸* 2.92 3.33 2.23 4.10 2.38 2.27 2.18 2.59 2.31 2.96 3.02 3.25 2.73 甘蔗秸 5.02 4.75 4.84 5.83 5.52 5.59 6.67 6.41 8.35 8.55 8.46 9.48 8.65 甜菜秸 1.60 1.19 1.38 1.47 0.85 1.07 0.61 0.78 0.88 0.71 1.06 0.91 0.79 果蔬秸 5.66 6.13 6.61 7.08 7.56 8.03 8.80 9.19 9.24 10.09 11.05 11.94 12.73 注:*表示不适宜饲料加工的作物. 表 3 2015年我国各地作物秸秆资源质量、热量和谷物当量多形态利用价值估算
Table 3. Calculation of crop straw polymorphous utilization values in weight, energy and cereal equivalent forms of provinces and cities in China in 2015
编码 地区 质量/ (109 kg) 能量/ (1016 J) 可饲谷物当量/ (109 kg) A 北京 0.74 0.86 0.62 B 上海 1.18 1.40 1.02 C 西藏 1.34 1.91 1.38 D 青海 1.67 2.30 1.67 E 天津 1.96 2.54 1.77 F 海南 2.40 2.29 1.66 G 宁夏 3.60 4.88 3.53 H 福建 6.26 7.65 5.44 I 浙江 7.83 9.73 6.99 J 重庆 10.67 14.21 10.22 K 山西 12.29 17.10 12.34 L 甘肃 12.30 16.80 12.04 M 陕西 12.39 17.91 12.81 N 贵州 12.54 16.58 11.76 O 广东 16.57 17.19 12.42 P 辽宁 19.07 25.37 18.37 Q 江西 19.64 26.80 19.03 R 云南 23.61 27.13 19.01 S 新疆 27.31 36.94 16.41 T 内蒙古 30.17 41.45 30.03 U 湖南 30.79 41.10 29.17 V 湖北 31.63 42.79 30.03 W 吉林 32.63 46.18 33.43 X 广西 33.54 23.52 17.00 Y 四川 36.13 49.05 35.26 Z 江苏 36.32 49.09 35.22 AA 安徽 37.18 52.32 37.15 AB 河北 37.94 49.71 34.91 AC 山东 52.82 70.86 49.71 AD 黑龙江 54.95 78.39 56.72 AE 河南 67.38 93.92 67.43 注:研究地区仅包括我国大陆部分. -
[1] DIEP N Q, FUJIMOTO S, MINOWA T, et al.Estimation of the potential of rice straw for ethanol production and the optimum facility size for different regions in Vietnam[J].Applied Energy, 2012, 93(5):205-211. https://econpapers.repec.org/RePEc:eee:appene:v:93:y:2012:i:c:p:205-211 [2] SUMMERS M D, JENKINS B M, HYDE P R, et al.Biomass production and allocation in rice with implications for straw harvesting and utilization[J].Biomass and Bioenergy, 2003, 24(3):163-173. doi: 10.1016/S0961-9534(02)00132-0 [3] 李太平, 徐超.江苏省农作物秸秆资源能源化潜力与区域分布研究[J].江苏社会科学, 2011(5):234-237. https://mall.cnki.net/qikan-ZRZY201703009.htmlLI Taiping, XU Chao.The energy potential of the resource of crop straw and regional distribution study of Jiangsu Province[J].Jiangsu Social Sciences, 2011(5):234-237. https://mall.cnki.net/qikan-ZRZY201703009.html [4] 毕于运, 高春雨, 王亚静, 等.中国秸秆资源数量估算[J].农业工程学报, 2009, 25(12):211-217. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2009.12.037BI Yuyun, GAO Chunyu, WANG Yajing, et al.Estimation of straw resources in China[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2009, 25(12):211-217. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2009.12.037 [5] EKMAN A, WALLBERG O, JOELSSON E, et al.Possibilities for sustainable biorefineries based on agricultural residues-a case study of potential straw-based ethanol production in Sweden[J].Applied Energy, 2013, 102(2):299-308. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/257157518_Sustainable_biorefineries_based_on_agricultural_residues-A_case_study_of_potential_straw-based_ethanol_production_in_Sweden [6] 李幸芳, 李刚, 韩敏, 等.河南省农作物秸秆资源分布及其资源评价[J].河南科学, 2011, 29(12):1464-1469. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3918.2011.12.020LI Xingfang, LI Gang, HAN Min, et al.The research on the estimation of crop straw resource sistribution and the resource evaluation in Henan Province[J].Henan Science, 2011, 29(12):1464-1469. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3918.2011.12.020 [7] WANG Yajing, BI Yuyun, GAO Chunyu.The assessment and utilization of straw resources in China[J].Agricultural Sciences in China, 2010, 9(12):1807-1815. doi: 10.1016/S1671-2927(09)60279-0 [8] 郭冬生, 黄春红.近10年来中国农作物秸秆资源量的时空分布与利用模式[J].西南农业学报, 2016, 29(4):948-954. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90760A/201204/41787225.htmlGUO Dongsheng, HUANG Chunhong.Spatial and temporal distribution of crop straw resources in past 10 years in China and its use pattern[J].Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 29(4):948-954. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90760A/201204/41787225.html [9] 魏赛, 吕晶晶.我国粮食主产区秸秆资源量估算与利用[J].中国畜牧业, 2013(19):56-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2473.2013.19.014WEI Sai, LV Jingjing.Estimation and utilization of straw resources in China's main grain producing areas[J].China Animal Industry, 2013(19):56-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2473.2013.19.014 [10] BAO Jiancai, YU Jihua, FENG Zhi, et al.Situation of distribution and utilization of crop straw resources in seven western provinces, China[J].The Journal of Applied Ecology, 2014, 25(1):181-187. doi: 10.1007/s12155-017-9845-4 [11] 王亚静, 毕于运, 高春雨.中国秸秆资源可收集利用量及其适宜性评价[J].中国农业科学, 2010, 46(9):1852-1859. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90161X/201009/33750108.htmlWANG Yajing, BI Yuyun, GAO Chunyu.Collectable amounts and suitability evaluation of straw resource in China[J].Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2010, 46(9):1852-1859. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90161X/201009/33750108.html [12] 蔡亚庆, 仇焕广, 徐志刚.中国各区域秸秆资源可能源化利用的潜力分析[J].自然资源学报, 2011, 26(10):1637-1646. https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/28ea990177232f60ddcca1d6.htmlCAI Yaqing, QIU Huanguang, XU Zhigang.Evaluation on potentials of energy utilization of crop residual resources in different regions of China[J].Journal of Natural Resources, 2010, 26(10):1637-1646. https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/28ea990177232f60ddcca1d6.html [13] BAO Jiancai, YU Jihua, FENG Zhi, et al.Situation of distribution and utilization of crop straw resources in seven western provinces, China[J].Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2014, 25(1):181-187. doi: 10.1007/s12155-017-9845-4 [14] HONG Jinglan, REN Lijun, HONG Jingmin, et al.Environmental impact assessment of corn straw utilization in China[J].Journal of Cleaner Production, 2016, 112(2):1700-1708. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/273616971_Environmental_impact_assessment_of_corn_straw_utilization_in_China [15] MANEVSKI K, BORGESEN C D, LI Xiaoxin, et al.Optimising crop production and nitrate leaching in China:measured and simulated effects of straw incorporation and nitrogen fertilisation[J].European Journal of Agronomy, 2016, 80(10):32-44. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1161030116301228 [16] LI Qiang, HU Shanying, CHEN Dingjiang, et al.System analysis of grain straw for centralised industrial usages in China[J].Biomass and Bioenergy, 2012, 47(12):277-288. http://www.cabdirect.org/abstracts/20133048911.html [17] LIU Enhai, LIU Shengyong.Process optimization and study of biogas fermentation with a mixture of duck manure and straw[J].Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2017, 72(5):439-444. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1364032117300175 [18] DAROCH M, GENG Shu, WANG Guangyi.Recent advances in liquid biofuel production from algal feed stocks[J].Applied Energy, 2013, 102(2):1371-1381 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0306261912005533 [19] TRITIB S, SHABBIR H G.Potential alternatives of heat and power technology application using rice straw in Thailand[J].Applied Energy, 2010, 87(2):128-133. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/222828765_Potential_alternatives_of_heat_and_power_technology_application_using_rice_straw_in_Thailand [20] WILSON P, GLITHERO N J, RAMSDEN S J.Prospects for dedicated energy crop production and attitudes towards agricultural straw use:the case of livestock farmers[J].Energy Policy, 2014, 74(11):101-110. http://eprints.nottingham.ac.uk/37468 [21] ZHUANG Dafang, JIANG Dong, LIU Lei, et al.Assessment of bio-energy potential on marginal land in China[J].Renew Sust Energ Rev, 2011, 15(2):1050-1056. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2010.11.041 [22] 方放, 李想, 石祖梁, 等.黄淮海地区农作物秸秆资源分布及利用结构分析[J].农业工程学报, 2015, 31(2):228-234. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/yj/Detail/Periodical?id=Periodical_nygcxb201502032FANG Fang, LI Xiang, SHI Zuliang, et al.Analysis on distribution and use structure of crop straw resources in Huang-Huai-Hai Plain of China[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2015, 31(2):228-234. http://industry.wanfangdata.com.cn/yj/Detail/Periodical?id=Periodical_nygcxb201502032 [23] 马骁轩, 蔡红珍, 付鹏, 等.中国农业固体废弃物秸秆的资源化处置途径分析[J].生态环境学报, 2016, 25(1):168-174. http://d.g.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_tryhj201601025.aspxMA Yaoxuan, CAI Hongzhen, FU Peng, et al.Analysis of the reutilization methods for agricultural waste of straw in Chinas[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2016, 25(1):168-174. http://d.g.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_tryhj201601025.aspx [24] SONG Shizhong, LIU Pei, XU Jing, et al.Life cycle assessment and economic evaluation of pellet fuel from corn straw in China:a case study in Jilin Province[J].Energy, 2017, 130(7):373-381. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/273586456_Economic_environmental_and_social_assessment_of_briquette_fuel_from_agricultural_residues_in_China_-_A_study_on_flat_die_briquetting_using_corn_stalk [25] MONTELEONE M, CAMMERINO A R B, GAROFALO P, et al.Straw-to-soil or straw-to-energy? an optimal trade off in a long term sustainability perspective[J].Applied Energy, 2015, 154(4):891-899. https://econpapers.repec.org/RePEc:eee:appene:v:154:y:2015:i:c:p:891-899 [26] 曹志宏.基于能量转化的河南省作物秸秆养畜潜力研究[J].地域研究与开发, 2014, 33(4):163-167. http://c.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/dyyjykf/2014-4.aspxCAO Zhihong.The livestock potential estimation of crop straw in Henan Province from the perspective of energy conversion[J]. Areal Research and Development, 2014, 33(4):163-167. http://c.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/dyyjykf/2014-4.aspx [27] 李沛辰, 毋伟, 张丰松, 等.秸秆生物碳的结构特征及其对17β-雌二醇的吸附性能[J].环境科学研究, 2015, 28(8):1260-1266. http://www.hjkxyj.org.cn/hjkxyj/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20150812&flag=1LI Peichen, WU Wei, ZHANG Fensong, et al.Structural characteristics of straw biochars and sorption of 17β-estradiol on straw biochar[J].Research of Environmental Sciences, 2015, 28(8):1260-1266. http://www.hjkxyj.org.cn/hjkxyj/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20150812&flag=1 [28] 彭立群, 张强, 贺克斌.基于调查的中国秸秆露天焚烧污染物排放清单[J].环境科学研究, 2016, 29(8):1109-1118. http://www.hjkxyj.org.cn/hjkxyj/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20160802&flag=1PENG Liqun, ZHANG Qiang, HE Kebin.Emissions inventory of atmospheric pollutants from open burning of crop residues in China based on a national questionnaire[J].Research of Environmental Sciences, 2016, 29(8):1109-1118. http://www.hjkxyj.org.cn/hjkxyj/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20160802&flag=1 [29] 叶正. 中山市种植业生态系统能值分析[D]. 广州: 华南农业大学, 2001. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=Y406360 [30] 蓝盛芳, 钦佩, 陆宏芳.生态经济系统能值分析[M].北京:化学工业出版社, 2002:366-386. -






 下载:
下载: