Relationship between Microbial Diversity and Main Toxic Substances in Typical Refinery Wastewater
-
摘要: 为探明典型炼化废水处理系统(简称“系统”)生物毒性削减效果、主要致毒物质类别及微生物功能响应关系,以费氏弧菌和鼠伤寒沙门氏菌为受试生物,测试系统沿程生物急性毒性及遗传毒性,并结合毒性鉴别评价方法甄别系统主要致毒物质,同时利用高通量测序技术探究系统微生物功能结构与主要致毒物质响应关系. 结果表明:①系统沿程生物毒性总体呈下降趋势,生化处理单元进水为急性毒性微毒、遗传毒性阳性. 其中,炼油废水急性毒性总削减率为86.514%,遗传毒性总削减率为96.221%;化工废水急性毒性总削减率为53.281%,遗传毒性总削减率为62.273%. ②通过毒性鉴别评价方法(toxicity identification evaluation, TIE)结果推断,炼油废水主要致毒物质可能为阳离子金属及非极性有机物,化工废水主要致毒物质可能为阳离子金属. ③CCA分析表明,NH3-N浓度(r=0.819,p=0.001)、Cr浓度(r=0.777,p=0.002)、TPH (total petroleum hydrocarbon,总石油烃)浓度(r=0.752,p=0.002)与生化处理前微生物群落结构均呈显著正相关,与生化处理后微生物群落结构均呈显著负相关. ④生化处理阶段微生物功能发生极显著(p≤0.01)变化. FAPROTAX数据库预测可知,化学异养、好氧化学异养、芳香化合物降解、亚硝酸盐呼吸、硝酸盐还原、硝酸盐呼吸、氮气呼吸7种与碳、氮循环相关的微生物功能丰度均较高. 研究显示:系统沿程生物毒性虽呈下降趋势,但生化处理单元进水仍为急性毒性微毒、遗传毒性阳性;毒性表征推断炼油废水主要致毒物质可能为阳离子金属及非极性有机物,化工废水主要致毒物质可能为阳离子金属;生化处理单元中与碳、氮循环相关的微生物功能丰度较高,表明生化处理单元存在潜在毒性冲击风险.Abstract: In order to investigate the relationship between the biotoxicity reduction effect of a typical refinery wastewater treatment system (hereafter referred to as system), the main types of toxic substances and the response of functional microorganisms, Vibrio fischeri and Salmonella typhimurium were used as test organisms to examine the acute toxicity and genotoxicity with the process of the system. We used the toxicity identification evaluation (TIE) to identify the main toxic substances in the system, and used the high-throughput sequencing to explore the relationship between the microbial functional structure and the main toxic substances. The results showed that: (1) The biological toxicity showed a decreasing trend with the process in the system. The influent water of the biochemical treatment unit showed mild acute toxicity and positive in genotoxicity. The total reduction rate of acute toxicity of oil refinery wastewater was 86.514% and the total reduction rate of genotoxicity was 96.221%. The total reduction rate of acute toxicity of chemical wastewater was 53.281% and the total reduction rate of genotoxicity was 62.273%. (2) The TIE results indicated that the main toxic substances in oil refinery wastewater might be cationic metals and non-polar organic substances, and the main toxic substances in chemical wastewater might be cationic metals. (3) Canonical correlation analysis showed that the concentrations of ammonia (r=0.819, p=0.001), Cr (r=0.777, p=0.002) and total petroleum hydrocarbons (TPH) (r=0.752, p=0.002) were positively correlated with the microbial community structure before the biochemical treatment and negatively correlated with the microbial community structure after the biochemical treatment. (4) Microbial functions changed significantly during the biochemical treatment (p≤0.01). The FAPROTAX database predicted a high abundance of microorganisms in the carbon and nitrogen cycling in seven classes: chemoheterotrophy, aerobic chemoheterotrophy, aromatic compound degradation, nitrite respiration, nitrate reduction, nitrate respiration and nitrogen respiration. The study showed that although the biological toxicity along with the processes in the system decreased, the influent water of the biochemical treatment unit was still slightly toxic in acute toxicity and positive in genotoxicity. The characterization of the toxicity suggested that the main toxic substances in oil refinery wastewater were cationic metals and non-polar organic substances, and the main toxic substances in chemical wastewater were cationic metals. The abundance of functional microorganisms involved in carbon and nitrogen cycling in the biochemical treatment unit was high, indicating potential toxic risk in the biochemical treatment unit.
-
表 1 典型炼化废水各处理阶段出水的常规理化指标
Table 1. Physicochemical parameters of the typical refinery wastewater from different units
进水类型 处理阶段 pH 浓度/(mg/L) COD 硫化物 SS NH3-N TPH 炼油废水 进水 7.19±0.15 186.32±5.96 35.24±3.33 28.75±1.58 15.74±0.15 133.27±8.28 物理单元出水 7.44±0.22 202.76±10.24 10.56±1.05 20.17±2.75 21.38±2.24 85.15±8.01 生化单元出水 7.50±0.35 39.33±3.88 8.37±0.67 5.87±0.66 1.72±0.57 20.33±2.93 深度处理出水 7.17±0.52 33.24±5.27 0.35±0.045 3.22±0.15 0.15±0.033 0.35±0.019 化工废水 进水 7.23±0.65 136.57±15.29 15.28±2.66 22.74±2.78 14.01±1.66 35.99±7.45 生化单元出水 7.52±0.25 26.03±1.74 4.37±0.64 18.26±1.39 2.37±0.67 20.16±5.28 深度处理出水 7.19±0.39 23.34±1.05 0.59±0.037 12.15±1.07 0.24±0.046 3.52±0.68 注:《石油炼制工业污染物排放标准》(GB 31570—2015)中常规污染物理化指标排放限值分别为pH 6~9、COD浓度 60 mg/L、硫化物浓度1 mg/L、SS浓度70 mg/L、NH3-N浓度8 mg/L、TPH浓度5 mg/L. 表 2 工业废水生物毒性评价
Table 2. Biological toxicity evaluation of industrial wastewater
项目 毒性级别 TUa<0.40 无毒 0.40<TUa<1.00 微毒 1.00<TUa<10.00 中毒 10.00<TUa<100.00 高毒 TUa>100.00 剧毒 表 3 典型炼化废水各主要处理阶段生物毒性负荷削减率
Table 3. Reduction rate of biological toxicity load in main treatment stages of typical refinery wastewater
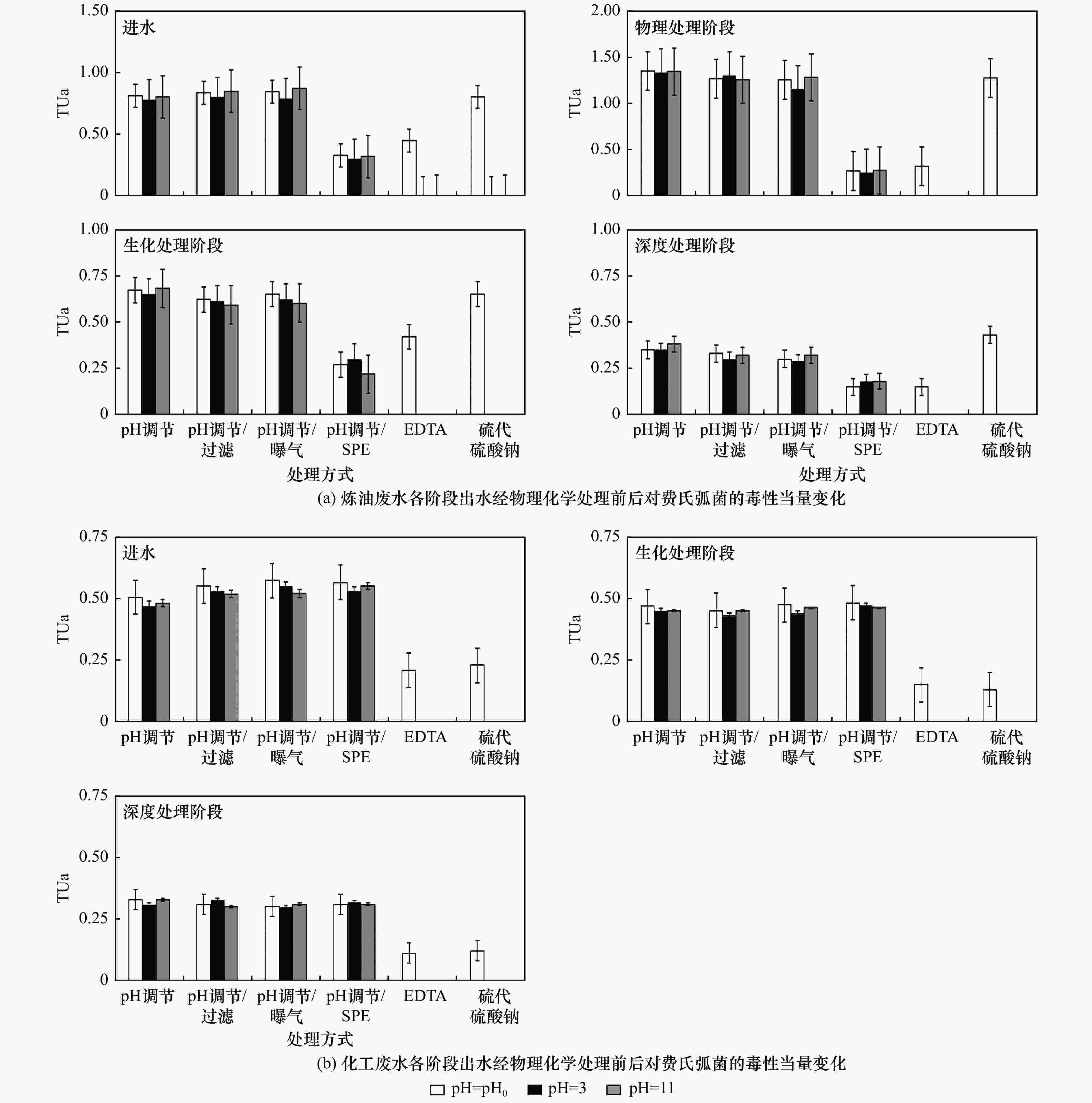
进水来源 主要处理阶段 生物毒性负荷削减率/% 急性毒性 遗传毒性 炼油废水 物理处理阶段 −4.267 72.334 生化处理阶段 72.792 53.281 深度处理阶段 52.462 70.762 总计 86.514 96.221 化工废水 生化处理阶段 7.382 44.597 深度处理阶段 28.181 31.905 总计 21.860 62.273 表 4 筛选后疑似致毒类环境因子的VIF值
Table 4. VIF values for suspected toxicogenic environmental factors after screening
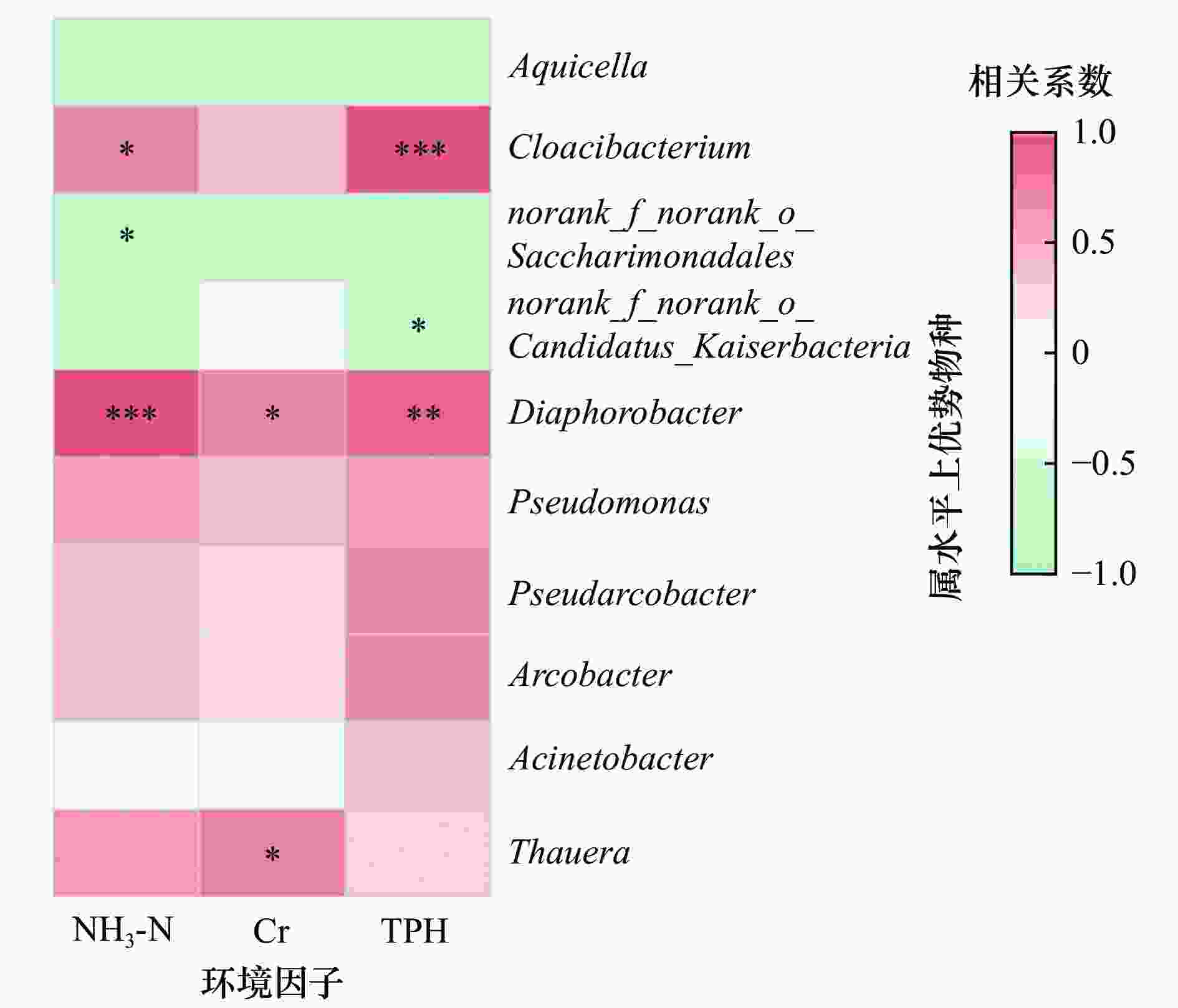
疑似致毒环境因子 VIF值 NH3-N 4.597 Cr 2.937 Ni 1.368 TPH 3.088 表 5 典型炼化废水生化处理阶段微生物功能丰度对比T检验
Table 5. T-test of the functional abundance of microorganisms in the biochemical treatment stage of typical refinery wastewater
样品编号 个案数 相关性 显著性(p) 炼油废水生化处理阶段进出水(BC) 20 0.703 0.01 化工废水生化处理阶段进出水(EF) 20 0.941 <0.01 -
[1] 生态环境部.中国生态环境状况公报:2020[R].北京:生态环境部,2021. [2] 张晶.常规生化处理对石化废水生物毒性及组分影响规律的研究[D].兰州:兰州大学,2012. [3] TEHRANI G M,SANY S B T,HASHIM R,et al.Predictive environmental impact assessment of total petroleum hydrocarbons in petrochemical wastewater effluent and surface sediment[J].Environmental Earth Sciences,2016,75(2):177. doi: 10.1007/s12665-015-4918-1 [4] RAM A,ROKADE M A,et al.A preliminary estimate of total petroleum hydrocarbons in water and some commercially important fish species in the amba estuary,west coast of India[J].Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology,2016,97(1):56-62. doi: 10.1007/s00128-016-1819-2 [5] BOTALOVA O,SCHWARZBAUER J,AL SANDOUK N.Identification and chemical characterization of specific organic indicators in the effluents from chemical production sites[J].Water Research,2011,45(12):3653-3664. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2011.04.012 [6] 高晶,张肖,赵乐军,等.用SOS/umu试验评价降雨径流遗传毒性的变化[J].生态毒理学报,2018,13(2):106-111. doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20171030001GAO J,ZHANG X,ZHAO L J,et al.The changes of genotoxicity in rainfall runoff based on SOS/umu test[J].Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology,2018,13(2):106-111. doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20171030001 [7] YU X,ZUO J E,TANG X Y,et al.Toxicity evaluation of pharmaceutical wastewaters using the Alga Scenedesmus obliquus and the bacterium Vibrio fischeri[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2014,266:68-74. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.12.012 [8] PLAHUTA M,TIŠLER T,TOMAN M J,et al.Toxic and endocrine disrupting effects of wastewater treatment plant influents and effluents on a freshwater isopod Asellus aquaticus (Isopoda,Crustacea)[J].Chemosphere,2017,174:342-353. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.01.137 [9] 宋佳宇,秦榕,杜显元,等.点源炼油废水处理系统微生物多样性及代谢功能研究[J].环境科学研究,2021,34(10):2389-2396. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2021.05.23SONG J Y,QIN R,DU X Y,et al.Microbial diversity and metabolic function in point source wastewater treatment system of oil refinery[J].Research of Environmental Sciences,2021,34(10):2389-2396. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2021.05.23 [10] WHALE G F,HJORT M,Di PAOLO C,et al.Assessment of oil refinery wastewater and effluent integrating bioassays,mechanistic modelling and bioavailability evaluation[J].Chemosphere,2022,287:132146. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132146 [11] WANG Y H,SHI X Y,HUANG X X,et al.Linking microbial community composition to farming pattern in selenium-enriched region:potential role of microorganisms on Se geochemistry[J].Journal of Environmental Sciences,2022,112:269-279. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2021.05.015 [12] 王宏洋,孙宇巍,王旭,等.美国针对高氯酸盐环境风险的管控策略及对我国的启示[J].环境科学研究,2022,35(10):2396-2403.WANG H Y,SUN Y W,WANG X,et al.Strategy of environmental risk control for perchlorate in the United States and enlightenment for China[J].Research of Environmental Sciences,2022,35(10):2396-2403. [13] GESTO M,TINTOS A,RODRÍGUEZ-ILLAMOLA A,et al.Effects of naphthalene,β-naphthoflavone and benzo(a)pyrene on the diurnal and nocturnal indoleamine metabolism and melatonin content in the pineal organ of rainbow trout,Oncorhynchus mykiss[J].Aquatic Toxicology,2009,92(1):1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2008.12.008 [14] 王立阳,李斌,李佳熹,等.沈阳市典型城市河流优先控制污染物筛选及生态环境风险评估[J].环境科学研究,2019,32(1):25-34. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2018.09.02WANG L Y,LI B,LI J X,et al.Priority pollutants and their ecological risk in typically urbanized river of Shenyang[J].Research of Environmental Sciences,2019,32(1):25-34. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2018.09.02 [15] NORBERG-KING T J,I.M D,DURHAN E J,et al.Methods for aquatic toxicity identification evaluations.Phase 1 toxicity: characterization procedures[R].New York:US Environmental Protection Agency,1991. [16] DURHAN E,NORBERG-KING T,BURKHARD L P.Methods for aquatic toxicity identification evaluations.phase Ⅱ toxicity:identification procedures for samples exhibiting acute and chronic toxicity[R].New York:US Environmental Protection Agency,Office of Research and Development,Environmental Research Laboratory,1993. [17] MOUNT D I,NORBERG-KING T J.Methods for aquatic toxicity identification evaluations.phase Ⅲ toxicity:confirmation procedures for samples exhibiting acute and chronic toxicity[R].New York:US Environmental Protection Agency,1993. [18] 陈学勇,韦朝海.点源有机毒物污(废)水排放的生态风险管理技术分析[J].化工进展,2010,29(2):342-349. doi: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2010.02.030CHEN X Y,WEI C H.Ecological risk assessment technology for point sources of organic toxicants from industrial and municipal effluents[J].Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2010,29(2):342-349. doi: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2010.02.030 [19] VARJANI S,JOSHI R,SRIVASTAVA V K,et al.Treatment of wastewater from petroleum industry:current practices and perspectives[J].Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2020,27(22):27172-27180. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-04725-x [20] 乔宇,闫振飞,冯承莲,等.基于文献计量学的环境内分泌干扰物研究热点分析[J].环境科学研究,2022,35(2):424-434. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2021.11.16QIAO Y,YAN Z F,FENG C L,et al.Research focus analysis of endocrine disrupting chemicals(EDCs) based on bibliometrics[J].Research of Environmental Sciences,2022,35(2):424-434. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2021.11.16 [21] 王业耀,姜明岑,李茜,等.流域水质预警体系研究与应用进展[J].环境科学研究,2019,32(7):1126-1133. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2019.05.01WANG Y Y,JIANG M C,LI Q,et al.Advances in watershed water quality early-warning system[J].Research of Environmental Sciences,2019,32(7):1126-1133. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2019.05.01 [22] 吴慧君,宋权威,郑瑾,等.微生物降解石油烃的功能基因研究进展[J].微生物学通报,2020,47(10):3355-3368. doi: 10.13344/j.microbiol.china.200402WU H J,SONG Q W,ZHENG J,et al.Function genes in microorganisms capable of degrading petroleum hydrocarbon[J].Microbiology China,2020,47(10):3355-3368. doi: 10.13344/j.microbiol.china.200402 [23] 罗景阳,张乐,张腾,等.不同工艺对污水处理效能及细菌代谢功能的影响[J].中国给水排水,2021,37(23):61-67.LUO J Y,ZHANG L,ZHANG T,et al.Effects of different processes on wastewater treatment efficiency and bacterial metabolic function[J].China Water & Wastewater,2021,37(23):61-67. [24] 刘灵婕,季民,王芬,等.反硝化深床滤柱深度脱氮效果及反硝化功能基因分析[J].化工进展,2018,37(12):4917-4923.LIU L J,JI M,WANG F,et al.Nitrogen removal performance of deep-bed denitrification filter and analysis of denitrifying genes[J].Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2018,37(12):4917-4923. [25] 言野,李娜,刘楠楠,等.利用改进的SOS/umu方法检测水处理过程中污染物的遗传毒性效应[J].生态毒理学报,2013,8(6):909-916. doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20121017001YAN Y,LI N,LIU N N,et al.Application of modified SOS/umu test to determine genotoxicity of genotoxic chemicals and effluents from drinking water treatment process[J].Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology,2013,8(6):909-916. doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20121017001 [26] MILLER J H.Experiments in molecular genetics[M].New York:Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory,1972. [27] 国家环境保护总局,水和废水监测分析方法编委会编.水和废水监测分析方法[M].4版.北京:中国环境科学出版社,2002:211-213. [28] de FMATOS M,BOTTA C M R,FONSECA A L.Toxicity Identification Evaluation (Phase I) of water and sediment samples from a tropical reservoir contaminated with industrial and domestic effluents[J].Environmental Monitoring and Assessment,2014,186(11):7999-8006. doi: 10.1007/s10661-014-3982-4 [29] ACIR I H,GUENTHER K.Endocrine-disrupting metabolites of alkylphenol ethoxylates:a critical review of analytical methods,environmental occurrences,toxicity,and regulation[J].Science of the Total Environment,2018,635:1530-1546. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.079 [30] 李娜,骆坚平,饶凯锋,等.用SOS/Umu生物测试评价北方某自来水厂对遗传毒性物质的去除效果[J].环境工程学报,2007,1(11):10-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9108.2007.11.003LI N,LUO J P,RAO K F,et al.Assessment of the effects of removal genotoxicity for a waterworks located in the north of China by using SOS/Umu test[J].Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering,2007,1(11):10-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9108.2007.11.003 [31] 陈玲,翁景霞,刘苏,等.工业废水毒性评估与致毒物质鉴别技术进展[J].环境监控与预警,2018,10(3):1-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6732.2018.03.001CHEN L,WENG J X,LIU S,et al.Progress on toxicity assessment and toxicant identification technique for industrial wastewater[J].Environmental Monitoring and Forewarning,2018,10(3):1-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6732.2018.03.001 [32] MALAKAHMAD A,HASANI A,EISAKHANI M,et al.Sequencing Batch Reactor (SBR) for the removal of Hg2+ and Cd2+ from synthetic petrochemical factory wastewater[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2011,191(1/2/3):118-125. [33] TORRES de LEMOS C,MILAN RÖDEL P,REGINA TERRA N,et al.River water genotoxicity evaluation using micronucleus assay in fish erythrocytes[J].Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2007,66(3):391-401. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2006.01.004 [34] 张瑛,曹迪,胡丽萍,等.某石化废水的综合毒性评价及其处理工艺对毒性的削减规律研究[J].生态毒理学报,2017,12(5):109-118. doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20170212001ZHANG Y,CAO D,HU L P,et al.Comprehensive toxicity evaluation and the effect of the treatment process on toxicity reduction of a petrochemical wastewater[J].Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology,2017,12(5):109-118. doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20170212001 [35] 黄利,陈文艳,万玉山,等.制革废水和印染废水的综合毒性评估及鉴别[J].环境科学,2015,36(7):2604-2609. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2015.07.037HUANG L,CHEN W Y,WAN Y S,et al.Comprehensive toxicity evaluation and toxicity identification used in tannery and textile wastewaters[J].Environmental Science,2015,36(7):2604-2609. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2015.07.037 [36] 王子健,骆坚平,查金苗.水体沉积物毒性鉴别与评价研究进展[J].环境污染与防治,2009,31(12):35-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2009.12.023WANG Z J,LUO J P,ZHA J M.A review on progress of sediment toxicity identification and evaluation[J].Environmental Pollution & Control,2009,31(12):35-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2009.12.023 [37] 赵建亮,方怡向,应光国.工业废水毒性鉴定评价方法体系的建议及其应用示例[J].生态环境学报,2011,20(3):549-559. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2011.03.028ZHAO J L,FANG Y X,YING G G.Toxicity identification and evaluation methodology proposed for various industrial effluents and its practical application[J].Ecology and Environmental Sciences,2011,20(3):549-559. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2011.03.028 [38] SULIASIH B A,OTHMAN M S,HENG L Y,et al.Toxicity identification evaluation of landfill leachate taking a multispecies approach[C].Southampton,UK:WIT Press,2010:311-322. [39] 马勇,黄燕,贾玉玲,等.发光细菌急性毒性测试方法的优化研究[J].环境污染与防治,2010,32(11):48-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2010.11.012MA Y,HUANG Y,JIA Y L,et al.Improved acute toxicity test method for luminescent bacteria[J].Environmental Pollution & Control,2010,32(11):48-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2010.11.012 [40] 刘旦宇,荣宏伟.石化乙烯工业废水中关键毒性物质的鉴别[J].环境工程,2012,30(4):101-104. doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.2012.04.031LIU D Y,RONG H W.Identification of the key toxicants in the petrochemical ethylene industrial wastewater[J].Environmental Engineering,2012,30(4):101-104. doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.2012.04.031 [41] KHARDENAVIS A A,KAPLEY A,PUROHIT H J.Simultaneous nitrification and denitrification by diverse Diaphorobacter sp.[J].Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology,2007,77(2):403-409. doi: 10.1007/s00253-007-1176-5 [42] NOUHA K,KUMAR R S,TYAGI R D.Heavy metals removal from wastewater using extracellular polymeric substances produced by Cloacibacterium normanense in wastewater sludge supplemented with crude glycerol and study of extracellular polymeric substances extraction by different methods[J].Bioresource Technology,2016,212:120-129. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2016.04.021 [43] LIU X R,DU M T,YANG J N,et al.Sulfite serving as a pretreatment method for alkaline fermentation to enhance short-chain fatty acid production from waste activated sludge[J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2020,385:123991. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.123991 [44] LI M Y,XU M M,SU A X,et al.Combined phenanthrene and copper pollution imposed a selective pressure on the rice root-associated microbiome[J].Frontiers in Microbiology,2022,13:888086. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.888086 [45] ETCHEBEHERE C,TIEDJE J.Presence of two different active nirS nitrite reductase genes in a denitrifying Thauera sp.from a high-nitrate-removal-rate reactor[J].Applied and Environmental Microbiology,2005,71(9):5642-5645. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.9.5642-5645.2005 [46] CHEN C M,MING J,YOZA B A,et al.Characterization of aerobic granular sludge used for the treatment of petroleum wastewater[J].Bioresource Technology,2019,271:353-359. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2018.09.132 [47] LI A D,LI L G,ZHANG T.Exploring antibiotic resistance genes and metal resistance genes in plasmid metagenomes from wastewater treatment plants[J].Frontiers in Microbiology,2015,6:1025. [48] ZHU X Z,LEE L W,SONG G Q,et al.Deciphering mono/multivalent draw solute-induced microbial ecology and membrane fouling in anaerobic osmotic membrane bioreactor[J].Water Research,2022,209:117869. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2021.117869 [49] WU M,WANG H M,WANG W Q,et al.The impact of heavy rain event on groundwater microbial communities in Xikuangshan,Hunan Province,P.R.China[J].Journal of Hydrology,2021,595:125674. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125674 [50] QU Z L,LIU B,MA Y,et al.Differences in bacterial community structure and potential functions among Eucalyptus plantations with different ages and species of trees[J].Applied Soil Ecology,2020,149:103515. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2020.103515 -





 下载:
下载: